Note: This problem statement includes images that may not appear
if you are using a plugin. For best results, use the Arena editor.
In the vector-drawing mode of the grafix software package, the
user plots geometric objects of three kinds: arcs, circles,
and polygons. These objects are grouped into collections known as
globs. A newly made object automatically belongs to a glob of which
it is the sole member. The user can later choose to merge two globs into
one, or to split one glob so that each of its objects is delegated to a
glob on its own. Each glob bears a unique identification number or ID,
which is crucial to updating the document. Your job
is to take a sequence of drawing instructions expressed in the grafix
internal language, and execute them according to the rules laid out below.
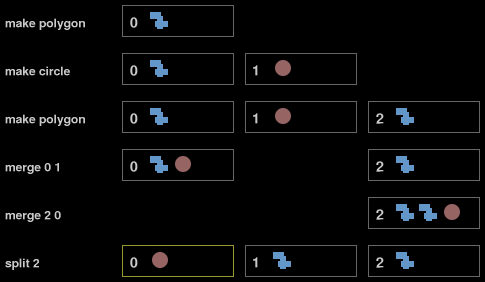
An instruction is a string that takes one the following forms.
make OBJ
delete ID
merge ID ID
split ID
In these forms, "OBJ" is a placeholder for one of the following values.
arc
circle
polygon
Furthermore, "ID" is a placeholder for the string representation of
an existing glob ID, which must be a non-negative integer. The string
representation will not be padded with zeros, and no instruction will
be padded with extraneous spaces on either side or between its tokens.
Before you execute the first instruction, the document is empty, so no
glob IDs are in use. When a "make" instruction is executed, you must
form a new glob whose ID is the lowest non-negative integer that isn't
currently in use as a glob ID. The sole member of the new glob will be
an object of the type named by the "make" instruction.
To execute a "delete" instruction, you take the glob whose ID is specified
by the instruction, discard all the objects it contains, and liberate its
ID for future use.
The "merge" instruction specifies two different IDs. The first one identifies
the target glob, to which you must add the members of the second glob, called
the source glob. Immediately thereafter, the source glob is to be destroyed and
its ID liberated. Note that globs do not contain other globs, but only objects. Thus,
the consequence of a merge operation is that the target glob contains more objects
than before, namely its prior contents as well as the objects drawn from the source glob.
The "split" instruction liberates the ID of the specified glob and then reassigns each of its member objects to an individual glob bearing the lowest available ID, in the following order. First the arcs are reassigned, then the circles, and finally the polygons. The specified glob is finally discarded. Its ID, if it was not reused by one of its member objects, remains available.
You are given a sequence of drawing instructions in the
String[] commands. After executing all instructions in
order, you are to determine the contents of the glob whose ID is specified
by the int sel. If there is no such glob, return
an empty int[]. Otherwise, return an int[]
with three values declaring, in order, the number of arcs, circles,
and polygons in that glob.
|