Note: This problem statement includes an image that may not appear
if you are using a plugin. For best results, use the Arena editor.
Dithering is the process whereby a bitmap drawn with a certain palette
or range of colors is converted to a visually similar bitmap using a
smaller palette. As a developer of the grafix software package, you must
implement a dithering algorithm that converts a grayscale image, drawn
with a palette of 256 color levels, to a black-and-white image, drawn with
a palette of 2 color levels. The grayscale image is the source,
while the eventual black-and-white image is the target.
One broad category of dithering algorithm is error diffusion, where the
difference in color level between a source pixel and the corresponding
target pixel, the so-called error, is distributed among the target
pixel's neighbors. Traditional error-diffusion methods distribute this
difference uniformly, which leads to unsightly directional artifacts
in the target image. The grafix package employs the Riemersma dither,
which diffuses the error in many different directions by following a
fractal path around the image.
The cardinal variant of the Riemersma dither, which you are to implement,
follows the Hilbert space-filling curve. A Hilbert curve is composed
of horizontal and vertical line segments that visit every cell in an
n-by-n grid such that n is a power of two, and n
is at least two. The curve is defined recursively, as illustrated below.
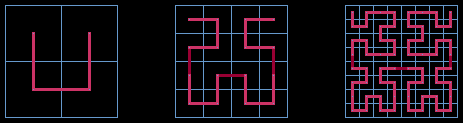
In the smallest case, a 2-by-2 grid, the Hilbert curve takes the form of a
cup made of three line segments, open at the top. To make
a Hilbert curve for the next smallest case, a 4-by-4 grid, we subdivide
each cell of the 2-by-2 grid into 2-by-2 child grids. In each of the child
grids, we form a child cup oriented and linked as above with respect to the parent
cup. To make an 8-by-8 grid, we subdivide each cell of the 4-by-4 grid into
2-by-2 child grids, orienting and linking each of the child cups similarly
with respect to its parent cup. This procedure is repeated as many times
as necessary.
In the context of Riemersma dithering, the Hilbert curve is understood as a path
leading from the top left pixel of a bitmap to the top right
pixel. The source image is guaranteed to have dimensions suitable for
a Hilbert curve. It will be passed to you as a String[]
containing the rows of a bitmap. In each
String, the contents of the row are represented by alphabetic characters,
which are mapped to color levels by the following scheme.
Characters 'a', 'b', 'c',..., 'z' correspond to color levels 0, 5, 10, ..., 125;
characters 'A', 'B', 'C',..., 'Z' correspond to color levels 130, 135, 140, ..., 255.
You are to return a String[] composed of the characters
'B' and 'W', corresponding to color levels 0 and 255, respectively.
The grafix implementation of Riemersma considers only the latest pixel for purposes of
error calculation. To begin with, the error value is set to zero, and dithering
begins at the top left pixel of the source image. The following procedure is carried out
when we visit a pixel.
The error is added to the current source pixel. If the source pixel now has a negative value, we set it to 0, and if it is greater than 255, we set it to 255. Otherwise, we leave the source pixel as it was after adding the error. If the source pixel is 127 or less, we set the corresponding target pixel to 0. Otherwise, we set the target pixel to 255. Now we subtract the value of the target pixel from that of the source pixel, and this difference becomes the new error value.
Then we move on to the next pixel along the Hilbert curve and repeat the procedure, halting only once we have dithered the final pixel in the top right corner of the image.
| 